Unveiling the Secrets of the Sahara: A Comprehensive Look at its Topography
Related Articles: Unveiling the Secrets of the Sahara: A Comprehensive Look at its Topography
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Secrets of the Sahara: A Comprehensive Look at its Topography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Secrets of the Sahara: A Comprehensive Look at its Topography

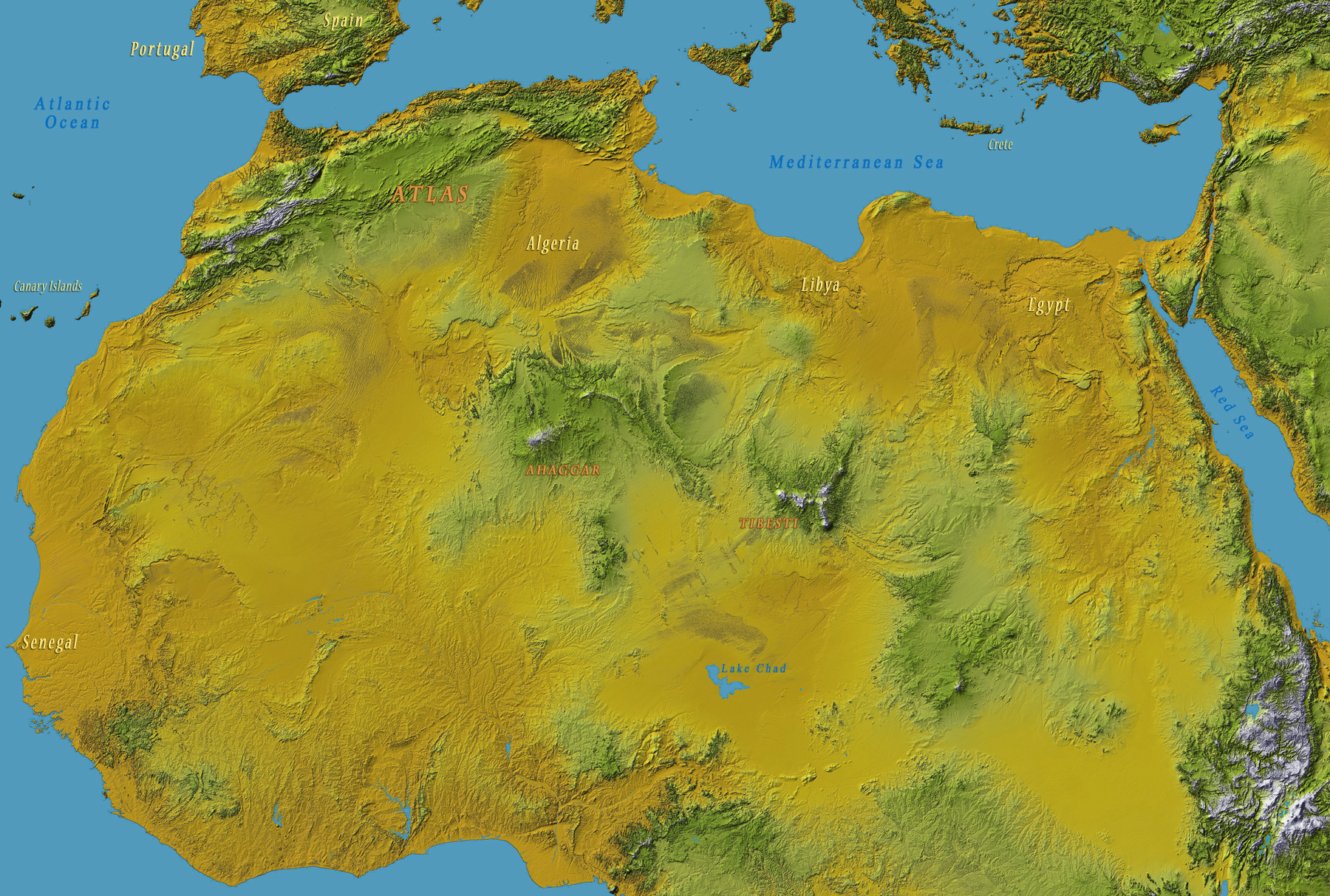
The Sahara Desert, the largest hot desert on Earth, is a vast and unforgiving landscape that stretches across northern Africa. Its topography is a testament to the interplay of geological forces, wind erosion, and climatic shifts over millennia. Understanding the Sahara’s diverse topography is crucial for appreciating its ecological complexities, its potential for resource exploitation, and its role in shaping the region’s history and culture.
A Landscape of Contrasts: Unveiling the Sahara’s Topographic Features
The Sahara’s topography is far from uniform. It is a mosaic of contrasting features, each with its unique characteristics and influence on the desert’s ecology and human activity.
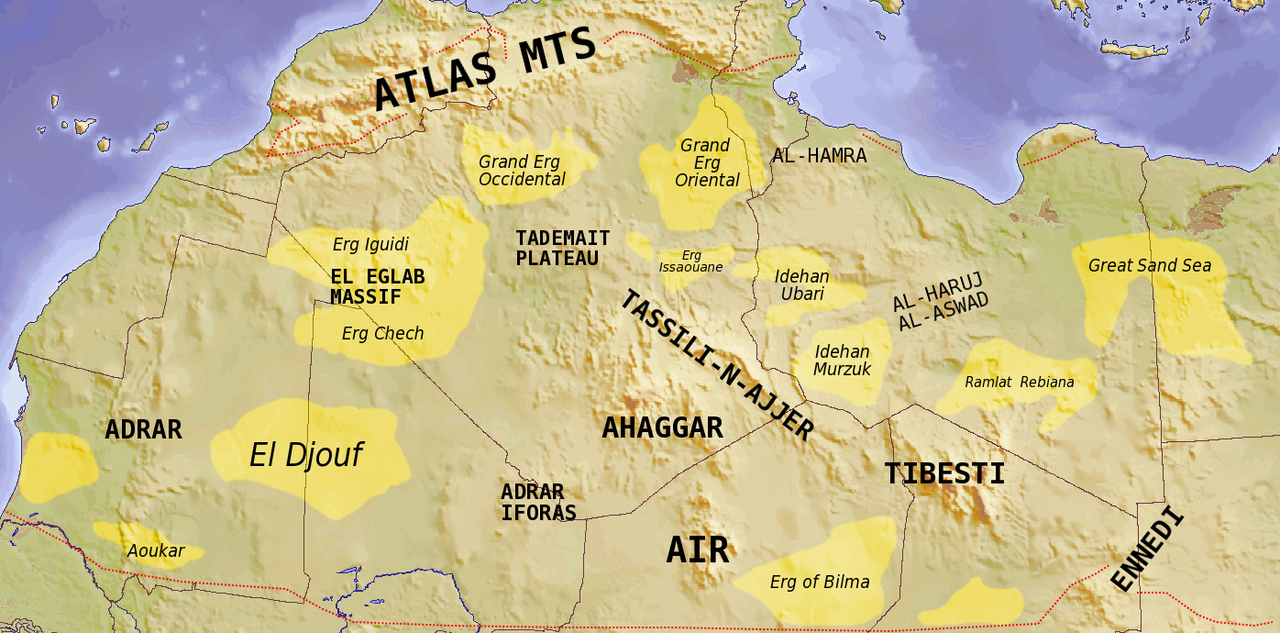
1. The Grand Erg: A Sea of Sand
The most prominent feature of the Sahara is its vast expanse of sand dunes, known as ergs. The Grand Erg Oriental and Grand Erg Occidental, located in Algeria and Libya respectively, are among the largest ergs in the world. These towering sand dunes, sculpted by wind, are a defining characteristic of the Sahara, creating a dynamic and ever-changing landscape.
2. The Hamadas: A Stony Wilderness
Scattered across the Sahara are vast plateaus of bare, rocky terrain known as hamadas. These elevated areas, often composed of sandstone or limestone, are characterized by their flat, hard surfaces and sparse vegetation. The Hamada du Draa in Morocco and the Hamada el Hamra in Algeria are prominent examples.
3. The Tassili n’Ajjer: A Plateau of Ancient Art
The Tassili n’Ajjer in southern Algeria is a unique plateau, rising to over 2,000 meters. This plateau, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is renowned for its remarkable rock art, depicting scenes of ancient life and climate change. The Tassili’s unique topography, characterized by jagged peaks, canyons, and arches, has preserved these ancient artistic treasures.
4. The Hoggar Mountains: A Volcanic Oasis
The Hoggar Mountains, located in central Algeria, are a volcanic mountain range that rises to over 3,000 meters. These mountains, with their rugged peaks and volcanic craters, provide a stark contrast to the surrounding desert plains. The Hoggar is a haven for biodiversity, supporting a unique ecosystem that thrives in the cooler, wetter conditions of higher altitudes.
5. The Aïr Mountains: A Plateau of Granite and Sandstone
The Aïr Mountains, located in northern Niger, are a plateau characterized by granite and sandstone formations. The Aïr’s rugged terrain, with its peaks, canyons, and valleys, has created a diverse range of microclimates, supporting a variety of plant and animal life.
6. The Libyan Desert: A Sea of Sand and Rock
The Libyan Desert, a vast and desolate region in eastern Libya, is characterized by its extensive sand dunes, rocky plateaus, and salt pans. The Libyan Desert is one of the driest and most inhospitable places on Earth, with extreme temperatures and scarce vegetation.
7. The Oases: Islands of Life in the Desert
Across the Sahara, scattered like emeralds in a sea of sand, are oases. These verdant pockets of life are sustained by underground water sources, providing fertile ground for agriculture and settlements. Oases, such as Siwa in Egypt and Ghardaia in Algeria, have played a vital role in sustaining human life and culture in the desert for millennia.
The Importance of Topography in Understanding the Sahara
The diverse topography of the Sahara plays a crucial role in shaping its environment, its resources, and its history.
1. Shaping the Climate: The Sahara’s topography influences its climate by creating microclimates and affecting wind patterns. Mountain ranges like the Hoggar and Aïr act as barriers, blocking moisture-laden winds and creating rain shadows on their leeward sides.
2. Influencing Biodiversity: The Sahara’s diverse topography supports a surprisingly rich biodiversity, with different plant and animal communities adapting to specific environments. The cooler, wetter conditions in the Hoggar and Aïr mountains, for example, support a variety of flora and fauna not found in the lower desert plains.
3. Resource Potential: The Sahara’s topography holds significant potential for resources. The ergs, for instance, are potential sources of sand for construction, while the hamadas contain deposits of minerals like iron and manganese. The underground water sources that sustain oases also hold the potential for irrigation and sustainable agriculture.
4. Shaping Human History: The Sahara’s topography has shaped human settlements, migration patterns, and trade routes. Oases have served as vital hubs for trade and cultural exchange, while the rugged terrain of the mountains has provided refuge for nomadic peoples.
5. Understanding Past Climate Change: The Sahara’s topography provides clues about past climate change. The rock art in the Tassili n’Ajjer, for instance, depicts scenes of a wetter Sahara, suggesting that the desert has undergone significant climatic shifts over time.
FAQs about the Sahara Desert Topography
1. How did the Sahara Desert form?
The Sahara Desert’s formation is a complex process involving tectonic activity, climate change, and wind erosion. The uplift of the Atlas Mountains in North Africa blocked moisture-laden winds from the Atlantic Ocean, leading to a gradual drying of the region. Over time, wind erosion shaped the landscape, creating the vast ergs, hamadas, and other topographic features.
2. What are the main types of sand dunes found in the Sahara?
The Sahara features a variety of sand dune types, including:
- Barchan dunes: Crescent-shaped dunes with horns pointing downwind.
- Transverse dunes: Long, linear dunes oriented perpendicular to the prevailing wind direction.
- Longitudinal dunes: Long, linear dunes oriented parallel to the prevailing wind direction.
- Star dunes: Pyramidal dunes with multiple arms extending in different directions.
3. Are there any permanent rivers in the Sahara Desert?
The Sahara Desert is generally very arid, with few permanent rivers. The Nile River, which flows through Egypt, is the only major river that crosses the Sahara. However, there are several ephemeral rivers, which flow only during periods of heavy rainfall.
4. What are the challenges of living in the Sahara Desert?
Living in the Sahara Desert presents a number of challenges, including:
- Extreme temperatures: The Sahara experiences very high temperatures during the day and very low temperatures at night.
- Scarcity of water: Water is a precious resource in the Sahara, and access to it is often limited.
- Harsh weather conditions: The Sahara is prone to sandstorms, dust storms, and other harsh weather conditions.
Tips for Exploring the Sahara Desert
1. Plan your trip carefully: The Sahara is a vast and unforgiving desert, so careful planning is essential. It is important to be aware of the weather conditions, the terrain, and the potential risks involved.
2. Travel with a guide: It is highly recommended to travel with a local guide who is familiar with the desert and its hazards. A guide can help you navigate the terrain, find water sources, and avoid dangerous situations.
3. Pack appropriate gear: Pack clothing that is lightweight, breathable, and protective from the sun. You will also need sturdy footwear, a hat, sunglasses, and sunscreen.
4. Be prepared for extreme temperatures: The Sahara experiences extreme temperatures, so it is important to stay hydrated and avoid strenuous activity during the hottest parts of the day.
5. Respect the environment: The Sahara is a fragile ecosystem, so it is important to respect the environment and leave no trace behind.
Conclusion
The Sahara Desert’s topography is a testament to the power of geological forces, wind erosion, and climatic shifts. Its diverse landscape, from towering sand dunes to rugged mountains and verdant oases, offers a glimpse into the complex interplay of nature and human history. Understanding the Sahara’s topography is essential for appreciating its ecological complexities, its potential for resource exploitation, and its role in shaping the region’s history and culture. By appreciating the unique features of this vast and unforgiving landscape, we can gain a deeper understanding of the Earth’s diverse and dynamic environments.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Secrets of the Sahara: A Comprehensive Look at its Topography. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!