Unveiling the Topography of Turkey: A Geographical Journey
Related Articles: Unveiling the Topography of Turkey: A Geographical Journey
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Topography of Turkey: A Geographical Journey. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Topography of Turkey: A Geographical Journey
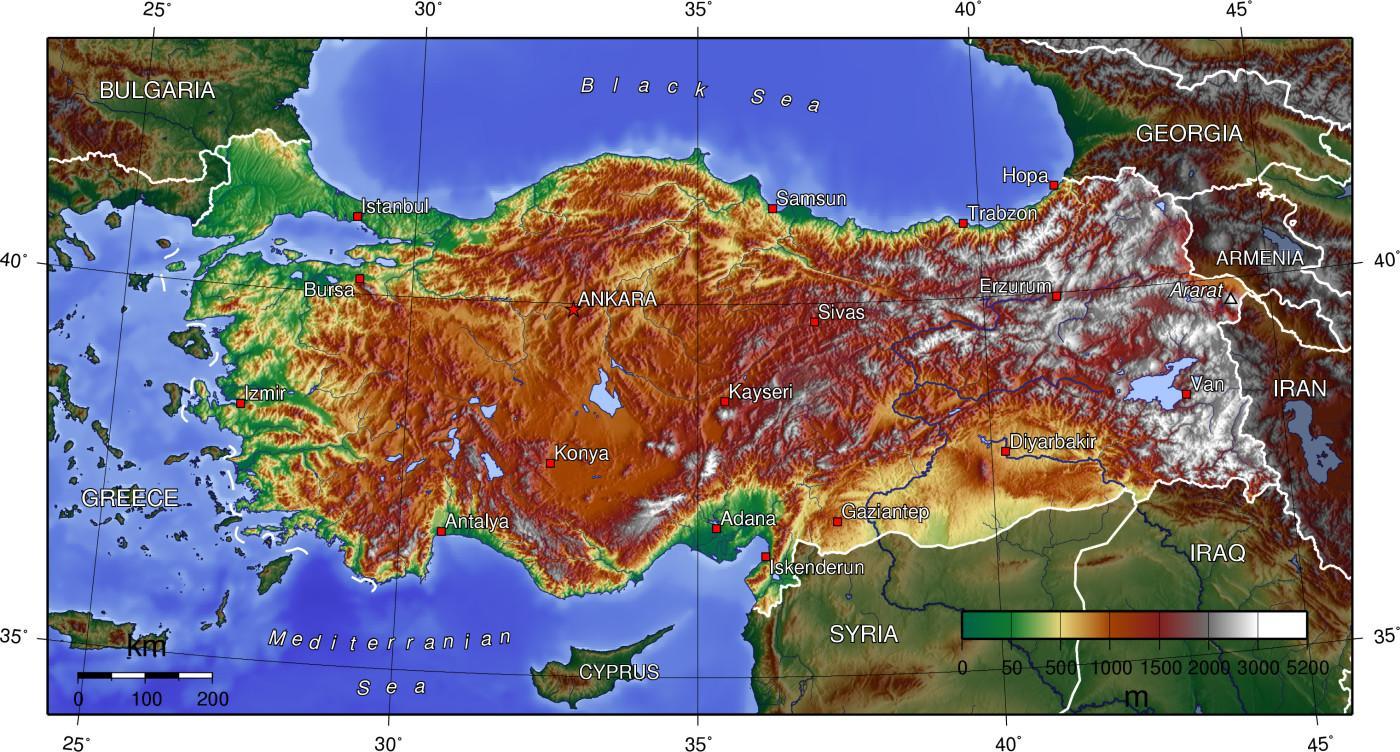
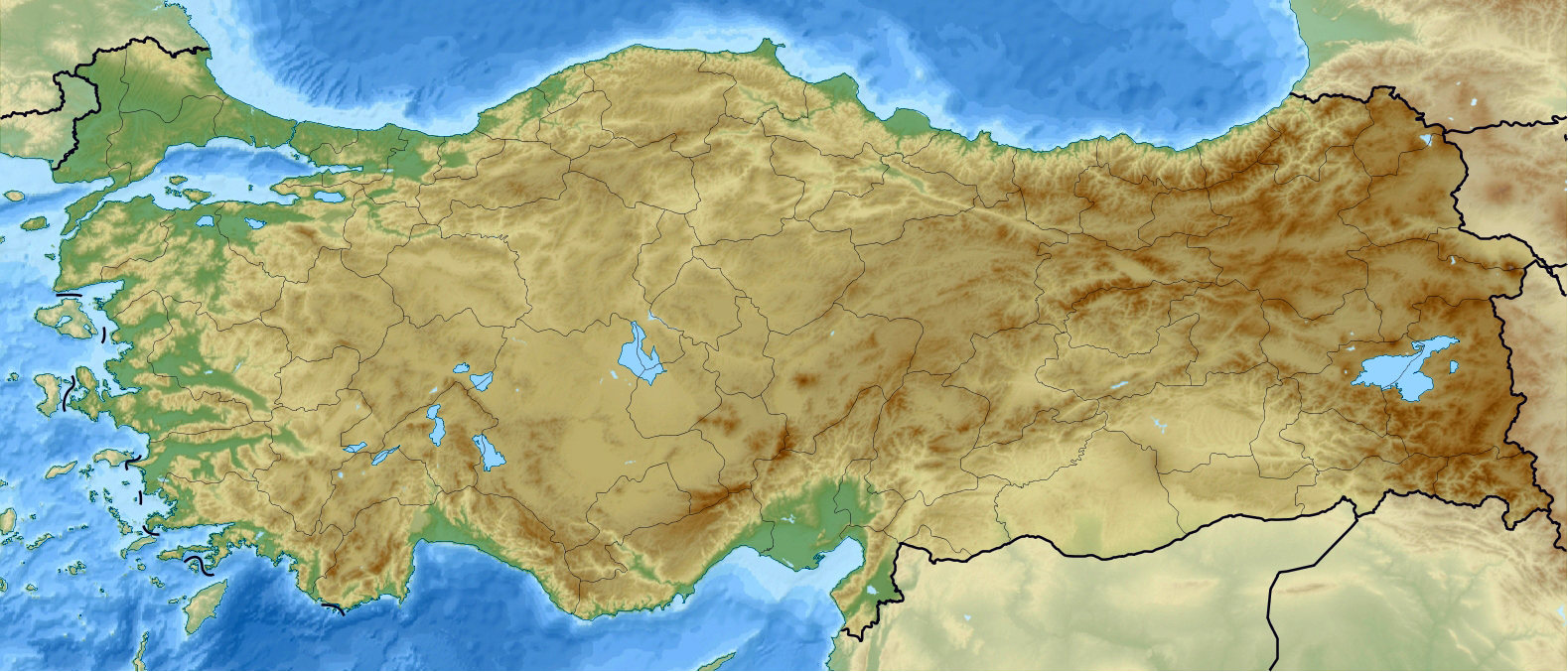
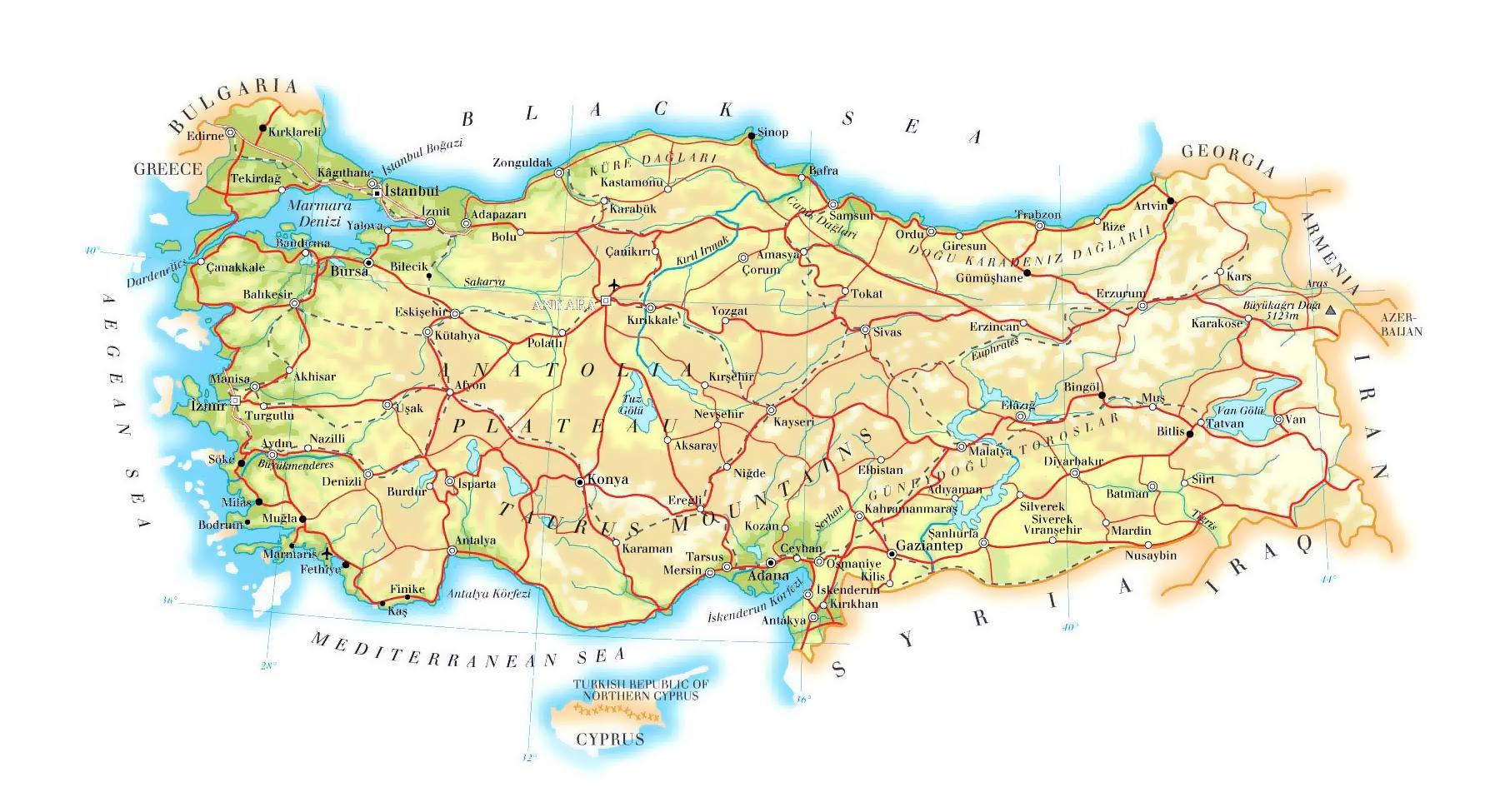
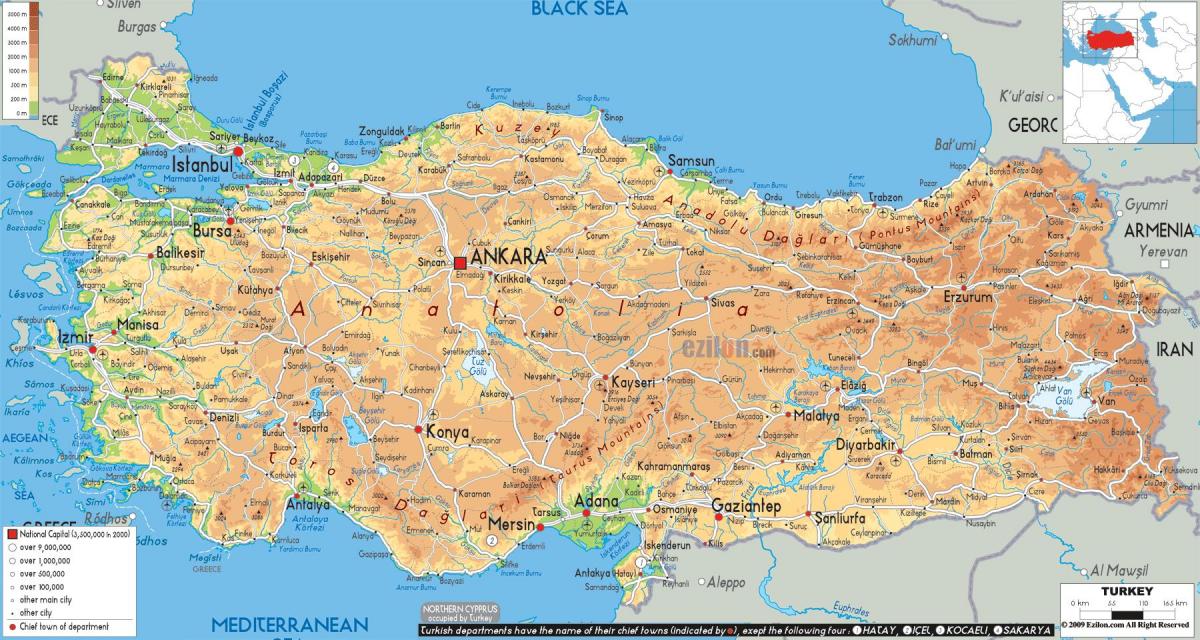
Turkey, situated at the crossroads of Europe and Asia, is a land of striking contrasts. Its diverse topography, from towering mountains to fertile valleys, from shimmering coastlines to arid plateaus, shapes its landscape, its climate, and its culture. A topographic map of Turkey, a visual representation of its elevation and landforms, provides a comprehensive understanding of this geographical complexity and its profound influence on the nation.
A Tapestry of Terrain
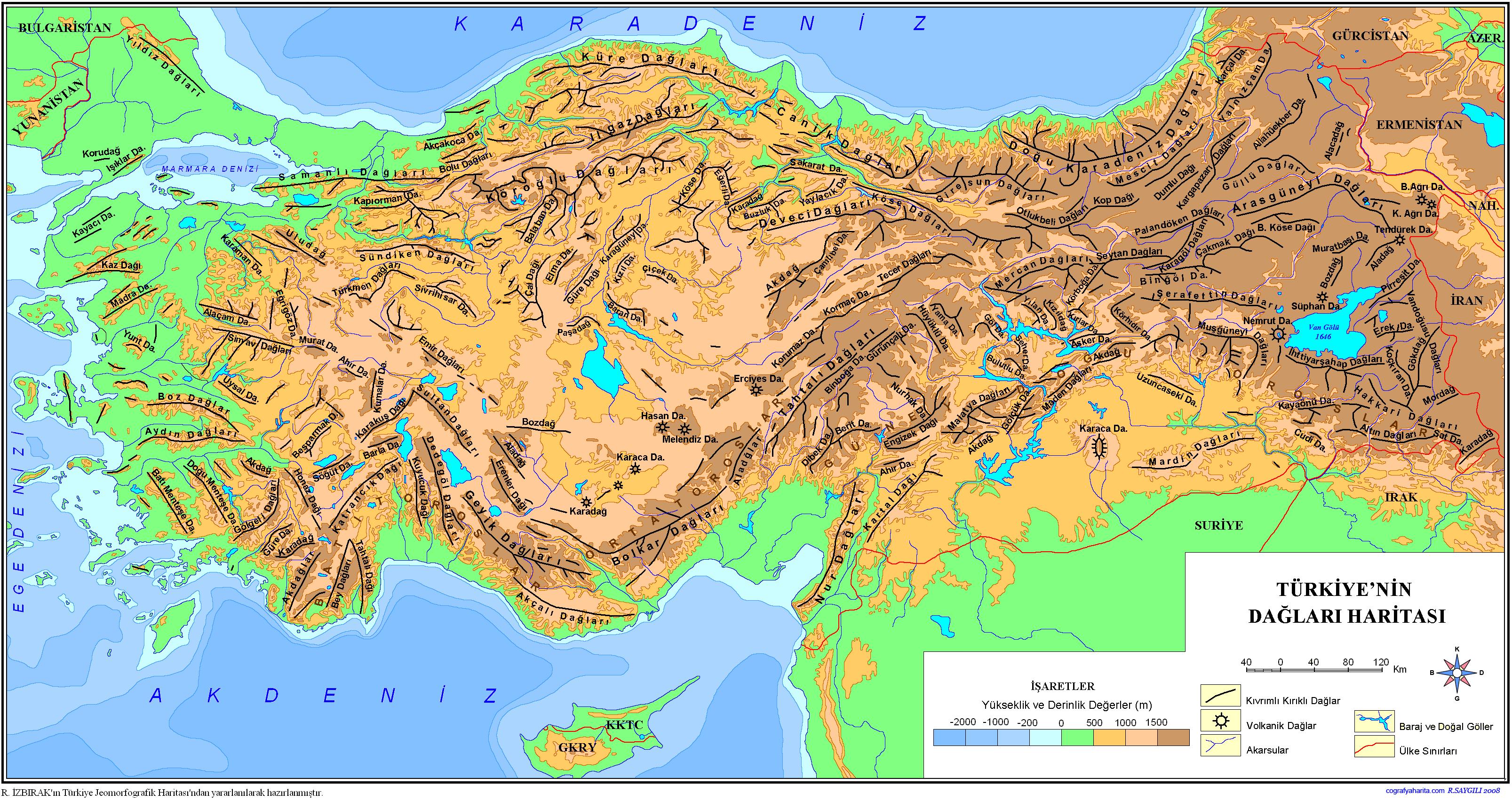
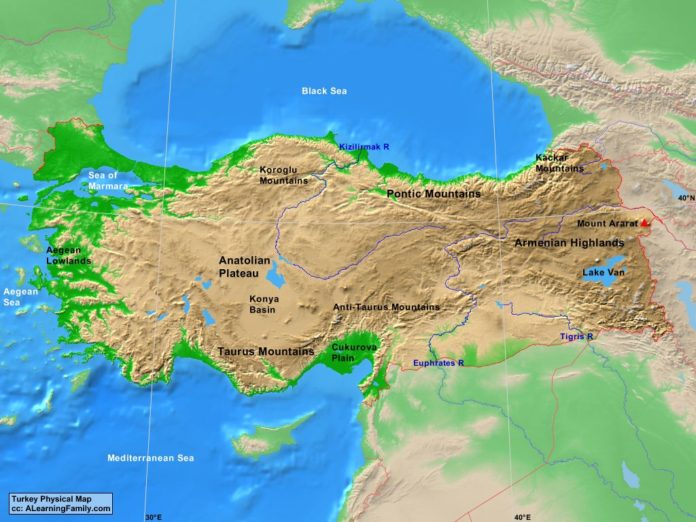
The topographic map reveals a Turkey characterized by its mountainous nature. The Anatolian Plateau, a vast, elevated expanse covering much of the country, is punctuated by a series of mountain ranges. The Pontic Mountains, rising along the Black Sea coast, form a formidable barrier, while the Taurus Mountains, stretching across the south, create a dramatic backdrop to the Mediterranean and Aegean coasts.
The map further highlights the presence of numerous volcanic peaks, including Mount Ararat, the highest point in Turkey and a symbol of national identity. The presence of these mountains and plateaus significantly influences Turkey’s climate, creating distinct regional variations. The Black Sea coast experiences a humid, temperate climate, while the Mediterranean and Aegean coasts enjoy warm, sunny summers and mild winters. The Anatolian Plateau, however, endures harsh continental conditions with cold winters and hot, dry summers.
The Flow of Rivers and Lakes
The intricate network of rivers and lakes, clearly depicted on the topographic map, plays a vital role in shaping Turkey’s geography. The Euphrates and Tigris rivers, originating in the eastern Anatolian Plateau, flow through the country before emptying into the Persian Gulf. The Kizilirmak, Turkey’s longest river, originates in the central Anatolian Plateau and flows northward to the Black Sea. These rivers serve as crucial sources of water for irrigation, hydropower generation, and transportation.
Turkey is also home to numerous lakes, including Lake Van, the largest lake in Turkey and the largest soda lake in the world. The topographic map reveals the geographical significance of these lakes, acting as natural reservoirs and contributing to the country’s biodiversity.
Coastal Landscapes and the Sea
The topographic map beautifully illustrates Turkey’s extensive coastline, stretching along the Black Sea, the Aegean Sea, and the Mediterranean Sea. The Aegean coast is characterized by its rugged coastline, dotted with numerous islands, while the Mediterranean coast boasts sandy beaches and turquoise waters. The Black Sea coast, on the other hand, features a more dramatic landscape with steep cliffs and lush forests.
These coastal regions are not only important for tourism and recreation but also play a critical role in Turkey’s economy, contributing to fishing, shipping, and maritime trade. The topographic map reveals the strategic importance of these coastlines, acting as gateways to international trade and connecting Turkey to the world.
Beyond the Topography: Human Impact
The topographic map serves as a foundation for understanding the human impact on the landscape. The distribution of settlements, infrastructure, and agricultural activities is closely linked to the topography. The fertile valleys and plains are ideal for agriculture, while the mountainous regions have historically been used for grazing and forestry.
The map also reveals the challenges posed by the topography, including the susceptibility to earthquakes and landslides. The presence of mountain ranges and fault lines makes Turkey prone to seismic activity, while the steep slopes and heavy rainfall can lead to soil erosion and landslides.
The Significance of a Topographic Map
The topographic map of Turkey is more than just a visual representation of its landforms. It serves as a powerful tool for understanding the country’s geography, its climate, its resources, and its challenges. This understanding is crucial for various sectors, including:
- Planning and Development: Topographic maps provide valuable data for urban planning, infrastructure development, and resource management. They help identify suitable locations for settlements, roads, dams, and other infrastructure projects, minimizing environmental impact and maximizing efficiency.
- Agriculture and Forestry: The topographic map assists in understanding the suitability of land for different agricultural practices and forestry activities. It helps identify areas prone to erosion, flooding, or drought, enabling farmers and foresters to adopt appropriate management practices.
- Disaster Management: Topographic maps are essential for disaster preparedness and response. They help identify areas vulnerable to earthquakes, floods, landslides, and other natural hazards, enabling authorities to develop effective mitigation strategies and emergency response plans.
- Tourism and Recreation: The topographic map provides valuable information for tourism development and recreation planning. It highlights scenic areas, hiking trails, and other attractions, facilitating the development of sustainable tourism initiatives.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the highest point in Turkey?
A: The highest point in Turkey is Mount Ararat, located in the eastern part of the country, with an elevation of 5,137 meters (16,854 feet).
Q: What is the largest lake in Turkey?
A: The largest lake in Turkey is Lake Van, situated in the eastern part of the country, with a surface area of 3,713 square kilometers (1,433 square miles).
Q: What are the major mountain ranges in Turkey?
A: The major mountain ranges in Turkey include the Pontic Mountains, the Taurus Mountains, and the Anatolian Plateau.
Q: What are the major rivers in Turkey?
A: The major rivers in Turkey include the Euphrates, the Tigris, and the Kizilirmak.
Q: What is the significance of Turkey’s coastline?
A: Turkey’s coastline is significant for its tourism, fishing, shipping, and maritime trade. It connects Turkey to the world and plays a crucial role in its economy.
Tips for Using a Topographic Map of Turkey
- Understand the Map Symbols: Familiarize yourself with the symbols used to represent different features, such as elevation, contour lines, rivers, and roads.
- Identify Key Features: Locate the major mountain ranges, rivers, lakes, and coastal areas.
- Analyze the Terrain: Observe the slopes, valleys, and plateaus to understand the topography and its impact on the landscape.
- Relate to Real-World Phenomena: Connect the topographic features to the climate, vegetation, settlements, and human activities.
- Use the Map in Conjunction with Other Resources: Combine the topographic map with other data sources, such as satellite imagery, climate maps, and population density maps, for a comprehensive understanding of the region.
Conclusion
The topographic map of Turkey is a powerful tool for understanding the country’s complex and diverse geography. It reveals the intricate interplay of landforms, climate, and human activity, shaping the nation’s landscape, resources, and cultural identity. By utilizing this map, we gain valuable insights into Turkey’s past, present, and future, paving the way for sustainable development, responsible resource management, and a deeper appreciation for this fascinating land.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Topography of Turkey: A Geographical Journey. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!