Unveiling Tonga: A Satellite’s Perspective
Related Articles: Unveiling Tonga: A Satellite’s Perspective
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Tonga: A Satellite’s Perspective. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling Tonga: A Satellite’s Perspective
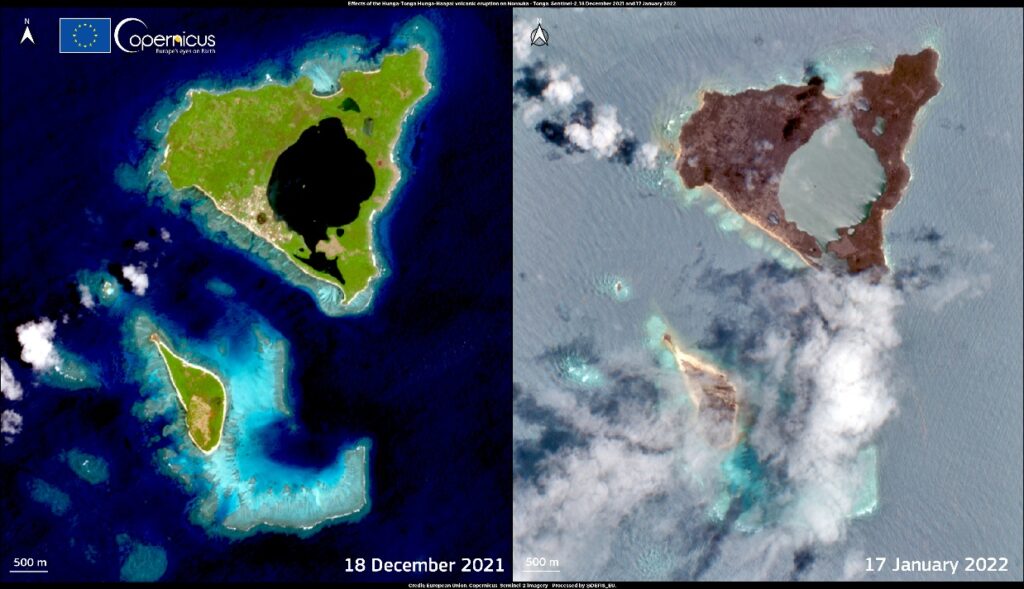
Tonga, an archipelago nation nestled in the vast expanse of the South Pacific, holds a captivating allure for explorers, scientists, and those seeking a glimpse into the heart of the Pacific realm. Understanding the intricate tapestry of its islands, its unique ecosystems, and its vulnerability to the forces of nature necessitates a comprehensive and dynamic approach. This is where satellite imagery, with its ability to capture vast landscapes from above, plays a crucial role.
A Window into Tonga’s Geography
Satellite maps of Tonga provide a powerful tool for visualizing the nation’s unique geographic features. The archipelago comprises over 170 islands and islets, with only about 36 inhabited. These islands are scattered across a vast area, stretching over 700,000 square kilometers of the Pacific Ocean.
Satellite imagery offers a detailed view of the diverse topography of Tonga. The volcanic origins of many islands are evident in the presence of towering peaks, active volcanoes, and rugged coastlines. Lush vegetation, indicative of the islands’ tropical climate, covers much of the landscape. The maps also reveal the intricate network of coral reefs that surround the islands, a vital component of Tonga’s marine ecosystem.
Beyond the Surface: Applications of Tonga Satellite Maps
The utility of satellite maps extends beyond simply visualizing Tonga’s landscape. They serve as valuable resources for a wide range of applications, influencing crucial aspects of life in Tonga and beyond.
1. Resource Management and Environmental Monitoring:
- Natural Disaster Assessment: Satellite images are invaluable for assessing the impact of natural disasters, such as cyclones and tsunamis. They can help map damage to infrastructure, identify areas affected by flooding, and guide relief efforts.
- Coastal Zone Management: Satellite data aids in monitoring coastal erosion, changes in coral reef health, and the impact of human activities on marine ecosystems. This information is crucial for developing sustainable management strategies for Tonga’s valuable coastal resources.
- Forestry and Land Use: Satellite images help track deforestation, monitor agricultural land use, and identify areas prone to land degradation. This information is essential for sustainable land management practices and conservation efforts.
2. Infrastructure Development and Planning:
- Transportation Planning: Satellite maps assist in identifying suitable locations for roads, ports, and airports, minimizing environmental impact and maximizing efficiency.
- Urban Planning: Satellite imagery aids in understanding urban growth patterns, identifying areas for development, and planning for future infrastructure needs.
- Telecommunications and Connectivity: Satellite data can help map areas with limited connectivity, guiding the deployment of telecommunications infrastructure for improved communication and access to information.
3. Scientific Research and Climate Change Monitoring:
- Oceanographic Studies: Satellite data provides insights into ocean currents, water temperature, and sea level changes, crucial for understanding the complex marine environment surrounding Tonga.
- Climate Change Impacts: Satellite imagery helps track changes in sea ice, glaciers, and vegetation, providing valuable data for assessing the impact of climate change on Tonga’s environment.
- Biodiversity Monitoring: Satellite images can be used to monitor changes in biodiversity, identify areas of high ecological value, and guide conservation efforts.
4. Tourism and Recreation:
- Tourism Development: Satellite maps help identify scenic areas, potential tourist attractions, and areas suitable for tourism infrastructure development.
- Marine Tourism: Satellite imagery assists in mapping coral reefs, shipwrecks, and other underwater features, enhancing the appeal of Tonga for diving and snorkeling enthusiasts.
FAQs: Addressing the Queries Surrounding Tonga Satellite Maps
1. What types of satellite data are used to create maps of Tonga?
A range of satellite data is employed, including optical imagery, radar data, and thermal infrared data. Optical imagery captures visible light, providing detailed views of the land surface. Radar data penetrates clouds and darkness, useful for mapping topography and vegetation. Thermal infrared data detects heat emissions, providing insights into surface temperature and volcanic activity.
2. How frequently are satellite images of Tonga updated?
The frequency of updates depends on the specific satellite and the type of data collected. Some satellites provide daily imagery, while others may update less frequently. The frequency of updates is crucial for tracking changes in the environment, responding to emergencies, and monitoring long-term trends.
3. What are the limitations of satellite maps for Tonga?
While powerful, satellite maps have limitations. Cloud cover can obscure the land surface, impacting the quality of imagery. Resolution limitations may not capture fine details, particularly in densely forested areas. Data processing and interpretation require expertise and specialized software.
4. How can I access satellite maps of Tonga?
Various online platforms offer access to satellite imagery, including Google Earth, NASA Worldview, and commercial providers such as Planet Labs. Some government agencies and research institutions also provide access to specific data sets.
Tips for Utilizing Tonga Satellite Maps Effectively
- Identify the purpose of your analysis: Clearly define your objectives to select the appropriate data type and resolution.
- Understand the limitations of the data: Be aware of factors such as cloud cover, resolution, and data accuracy.
- Utilize specialized software: Geographic Information Systems (GIS) software facilitates data processing, analysis, and visualization.
- Collaborate with experts: Seek assistance from specialists in remote sensing, geography, or relevant fields for accurate data interpretation and analysis.
Conclusion: A Powerful Tool for Understanding Tonga
Satellite maps offer an unparalleled perspective on Tonga, revealing its diverse landscape, its vulnerability to natural hazards, and its potential for sustainable development. By harnessing the power of satellite imagery, we can gain a deeper understanding of this island nation, contributing to informed decision-making, effective resource management, and the preservation of Tonga’s unique natural heritage. As technology advances, the role of satellite data in shaping Tonga’s future will continue to grow, providing a crucial tool for navigation, planning, and conservation in this captivating corner of the Pacific.
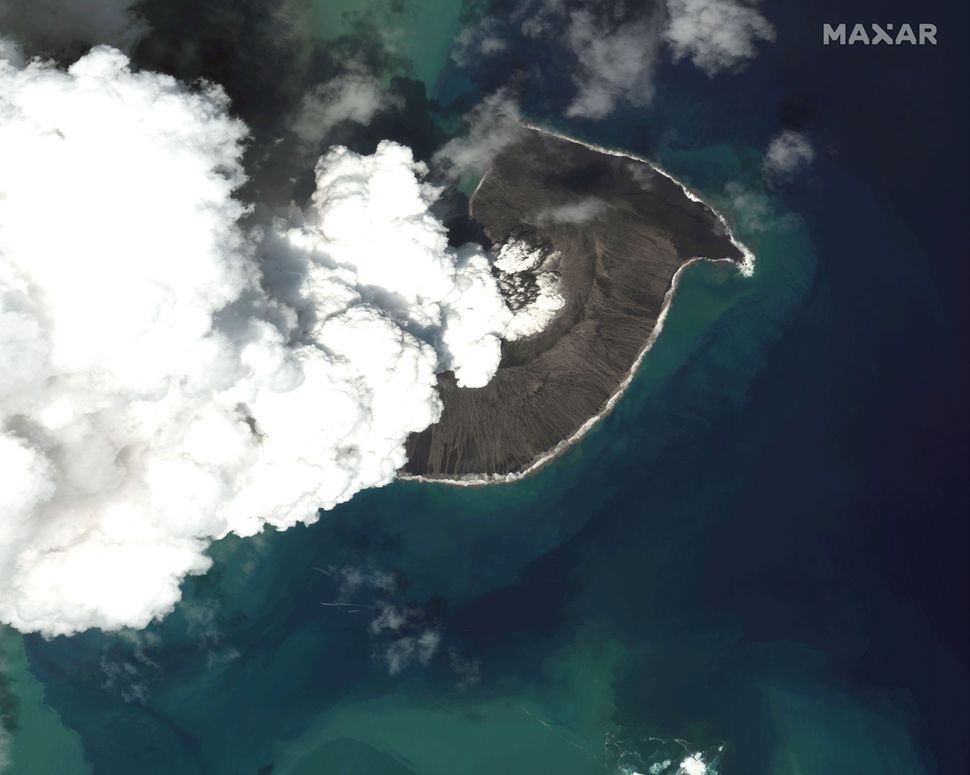
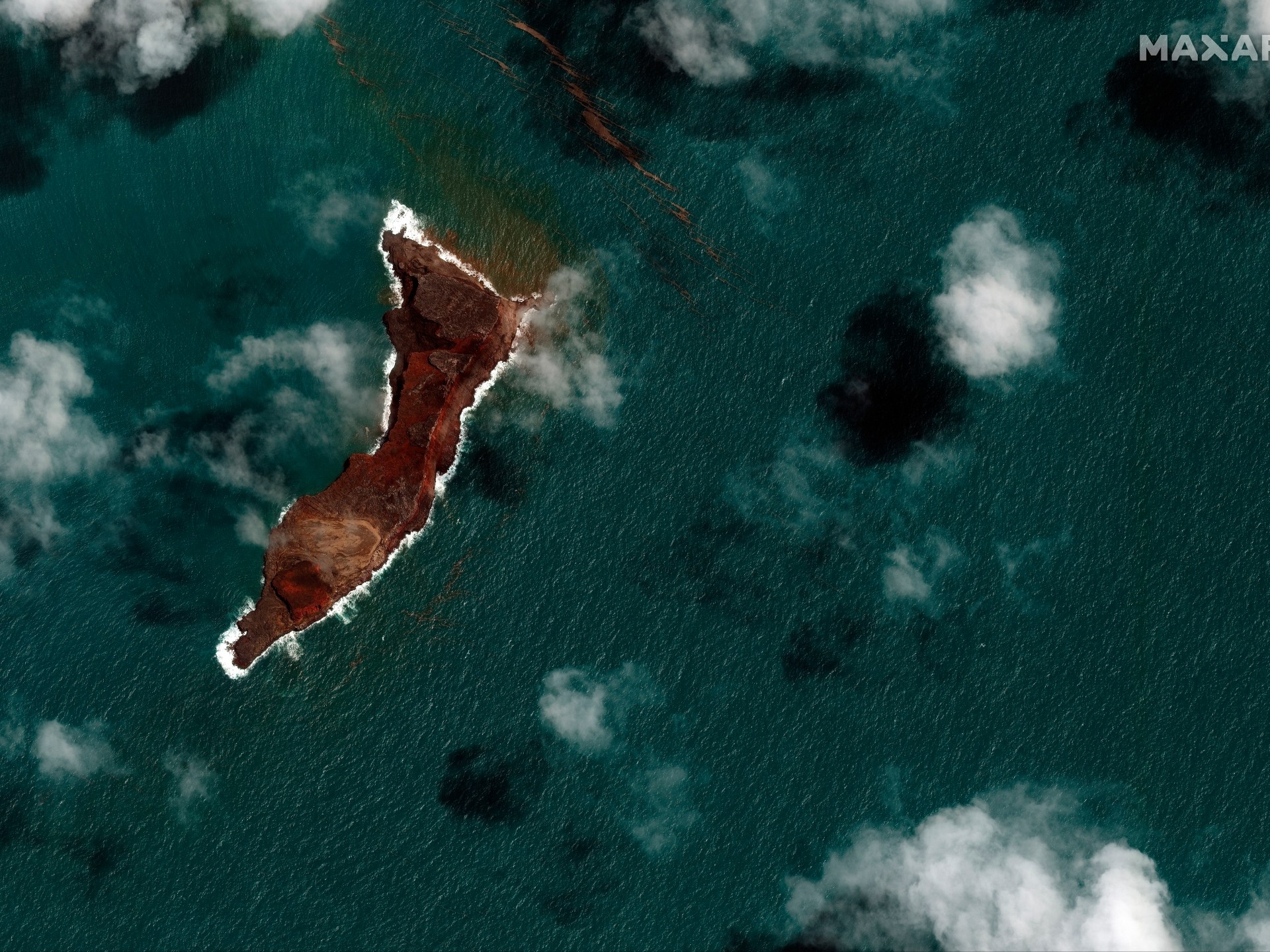








Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Tonga: A Satellite’s Perspective. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!