Vietnam’s Maritime Gateway: A Comprehensive Look at the Country’s Ports
Related Articles: Vietnam’s Maritime Gateway: A Comprehensive Look at the Country’s Ports
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Vietnam’s Maritime Gateway: A Comprehensive Look at the Country’s Ports. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Vietnam’s Maritime Gateway: A Comprehensive Look at the Country’s Ports
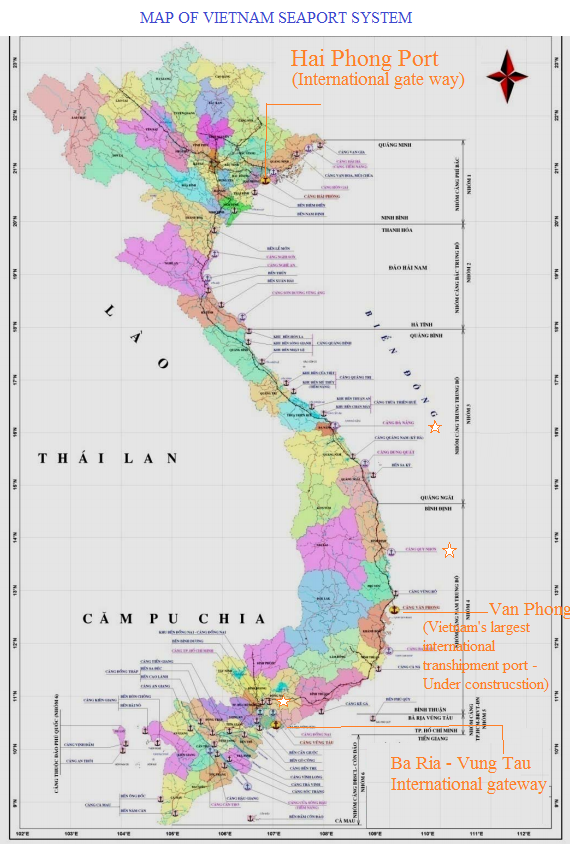
Vietnam, with its extensive coastline stretching over 3,260 kilometers, boasts a strategic location in Southeast Asia. This geographical advantage has fostered a thriving maritime industry, with its ports acting as vital hubs for international trade, economic growth, and regional connectivity. This article delves into the intricacies of Vietnam’s port network, exploring its structure, significance, and future prospects.
A Network of Strategic Hubs:
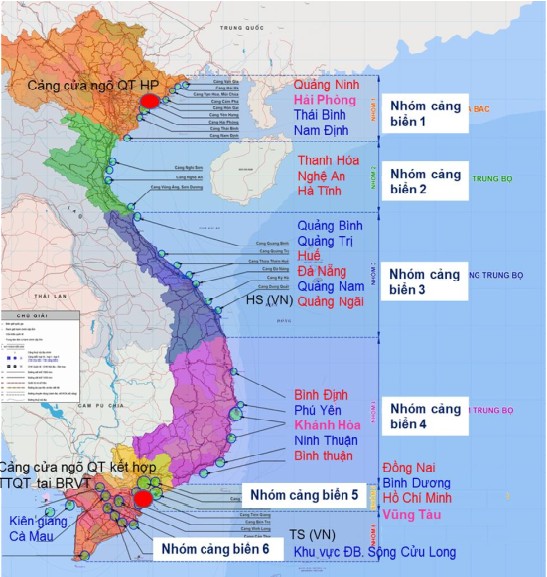
Vietnam’s port network comprises a diverse array of facilities catering to various needs. These range from large, deep-water container terminals handling trans-shipment cargo to smaller, specialized ports catering to specific industries like fishing, oil and gas, and agriculture.
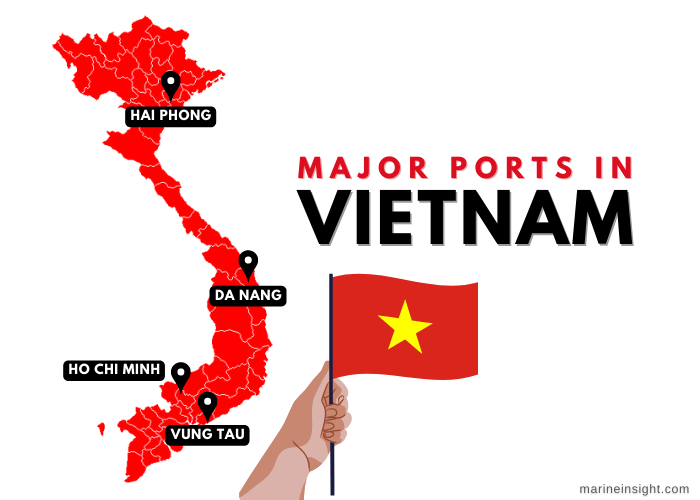
Major Ports and Their Roles:
-
Ho Chi Minh City Port (HCM Port): Located in the economic powerhouse of Ho Chi Minh City, HCM Port is Vietnam’s busiest port, handling a significant volume of containerized cargo, bulk goods, and general merchandise. Its strategic location near the Mekong Delta, a major agricultural region, makes it a crucial gateway for agricultural exports.
-
Hai Phong Port: Situated in the northern region of Vietnam, Hai Phong Port serves as a primary gateway for imports and exports to and from northern Vietnam and neighboring countries like China. It handles a diverse range of cargo, including industrial goods, machinery, and consumer products.
-
Da Nang Port: Located in the central region of Vietnam, Da Nang Port is a crucial hub for regional trade, handling both containerized cargo and bulk goods. Its strategic location near the East Sea (South China Sea) makes it a significant port for maritime trade with countries in the Asia-Pacific region.
-
Vung Tau Port: Located in the southern region of Vietnam, Vung Tau Port is a major oil and gas port, handling crude oil and refined petroleum products. It also serves as a key port for the export of seafood and other agricultural products.
The Importance of Vietnam’s Ports:
-
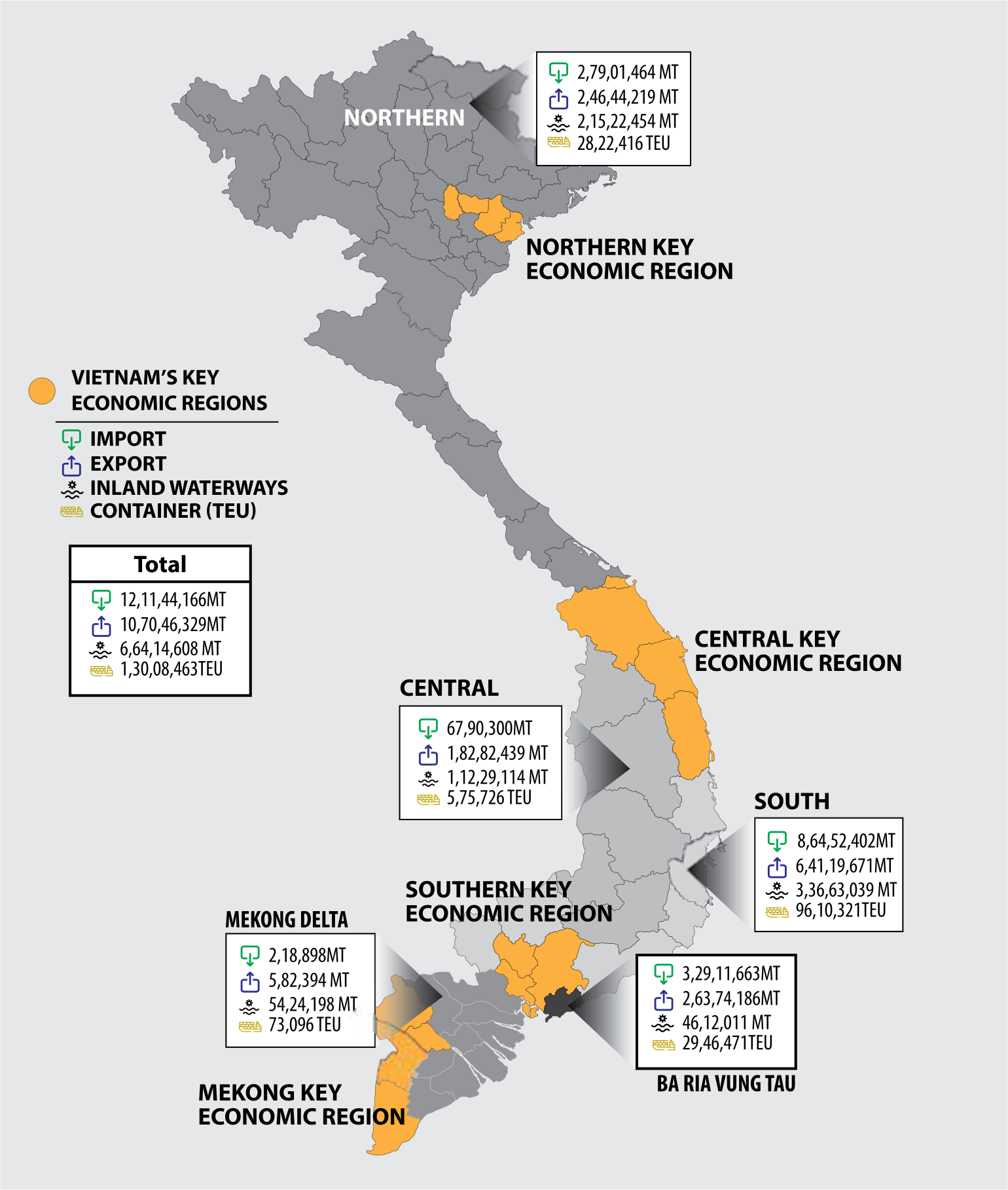
Economic Engine: Vietnam’s ports play a pivotal role in the country’s economic growth. They facilitate the import of raw materials and machinery, essential for industrial development, and export finished goods, contributing to Vietnam’s manufacturing and agricultural sectors.
-
Regional Trade Hub: Vietnam’s strategic location has positioned its ports as crucial links in regional trade networks. They connect Vietnam to major economies in Southeast Asia, East Asia, and beyond, fostering economic cooperation and growth.
-
National Security: Vietnam’s ports are vital for national security, providing access to vital resources and enabling the transportation of essential goods in times of emergency. They also play a crucial role in maritime security, contributing to the protection of Vietnam’s territorial waters and maritime interests.
Challenges and Opportunities:
-
Infrastructure Development: Vietnam’s port infrastructure, while steadily improving, still requires significant investment to meet the growing demands of international trade. Expanding capacity, upgrading facilities, and enhancing connectivity are key priorities.
-
Competition: Vietnam faces increasing competition from neighboring countries with well-established port infrastructure and robust maritime industries. Continuous innovation and efficiency improvements are crucial for maintaining competitiveness.
-
Sustainability: Vietnam’s ports are committed to sustainable practices, including reducing environmental impact, enhancing energy efficiency, and promoting responsible waste management. These initiatives are essential for long-term growth and environmental protection.
The Future of Vietnam’s Ports:
-
Technological Advancement: Vietnam’s ports are embracing technological advancements like automation, digitalization, and artificial intelligence to enhance efficiency, streamline operations, and improve competitiveness.
-
Investment in Infrastructure: The Vietnamese government is committed to investing in port infrastructure development, expanding capacity, and upgrading facilities to meet the growing demands of international trade.
-
Strategic Partnerships: Vietnam is actively pursuing strategic partnerships with international companies and organizations to enhance port operations, attract foreign investment, and foster technological collaboration.
FAQs about Vietnam’s Ports:
Q: What are the main types of cargo handled by Vietnamese ports?
A: Vietnamese ports handle a diverse range of cargo, including containerized goods, bulk cargo (like coal, iron ore, and grain), oil and gas products, general merchandise, and specialized cargo for specific industries.
Q: What are the key challenges faced by Vietnam’s port industry?
A: Vietnam’s port industry faces challenges such as infrastructure development, competition from neighboring countries, and the need for sustainable practices.
Q: What are the future prospects for Vietnam’s port industry?
A: Vietnam’s port industry is expected to grow significantly in the coming years, driven by technological advancements, infrastructure development, and strategic partnerships.
Tips for Businesses Using Vietnam’s Ports:
- Research and select the most suitable port: Consider factors like cargo type, location, capacity, and services offered.
- Engage with local authorities: Obtain necessary permits and licenses for smooth operations.
- Utilize available resources: Leverage the expertise of port operators, logistics providers, and government agencies.
- Stay informed about regulations and updates: Keep abreast of changes in port regulations and industry best practices.
Conclusion:
Vietnam’s ports are vital engines of economic growth, regional connectivity, and national security. Their strategic location, coupled with ongoing infrastructure development and technological advancements, positions them as key players in the global maritime industry. By leveraging its strengths and addressing challenges, Vietnam’s port network is poised for continued growth and success, contributing to the country’s economic prosperity and regional integration.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Vietnam’s Maritime Gateway: A Comprehensive Look at the Country’s Ports. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!